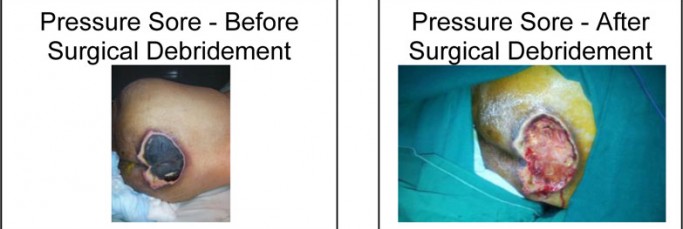
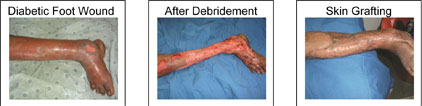
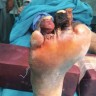
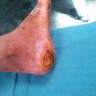
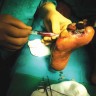
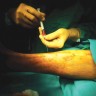
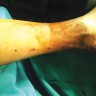
After debridement & regular dressings, once the wound is healthy (when it is a large wound) and once the infection is under control, your treating doctor may advise you for skin grafting for faster wound healing and to avoid deformities like scarring, contractures.
This will also give patients a good cosmetic covering.
When skin graft is placed on the weight bearing area i.e. plantar aspect or sole of the foot it is important to use special customized footwear to avoid pressure on the skin graft which may lead to break down & recurrent wounds over the pressure areas.
When a vital structure such as bone, # site with plates & screws, joints, tendons or nerves & blood vessels are exposed then a simple split thickness skin graft is not sufficient to cover the wound. The skin graft does not take (stick) on these bare & vital structures.
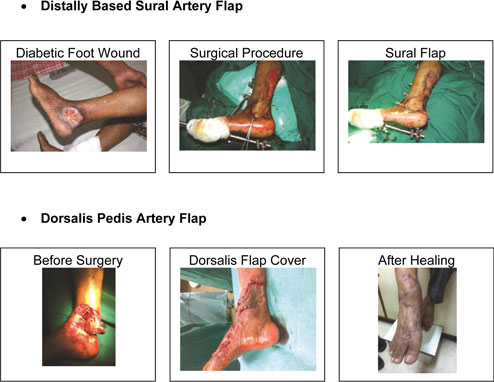
In such cases a more complicated procedure such as Fasciocutaneous Flap (full thickness skin with underlying fat) may be required to cover such defects in an attempt for limb salvage.
The various types of flaps include rotation or transposition flap or a flap based on particular artery such as Dorsalis Pedis artery or Sural Artery flap to name a few.
Flap brings more blood supply to the affected area controlling the infection & brings about faster healing.
Thus it helps in achieving a more functional result
Diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) are a significant and rapidly growing complication of diabetes. Over the past decade, the outcomes for patients with DFUs have not improved, despite advances in wound care. Successful treatment of diabetic foot ulcers is hindered by the lack of targeted therapy.
Stem cells are a promising treatment for DFUs as they are capable of targeting, as well as bypassing, the underlying abnormal healing mechanisms and deranged cell signalling in diabetic wounds and promote healing.
A particular type of stem cell, known as the mesenchymal stem cell (MSC), could increase wound healing when applied together with a bio-material made from collagen. Diabetic patients have an impaired ability to heal wounds and there is a critical need to develop new treatments to improve healing particularly in patients with foot ulcers.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are perhaps one of the most promising types of adult stem cell therapies currently being applied to wound healing. This is due in part to their differentiation potential and also because they are so accessible within the body. MSCs reside in many different tissues (bone marrow, fat tissue, umbilical cord, dermal layers of the skin) and are able to grow into a variety of different cell types, including skin cells. For the purposes of wound healing, MSCs are usually harvested from the bone marrow and grown in culture. A huge benefit of these cells is that they are immune response modulators.