Calluses
Condition and Causes
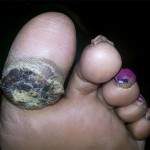
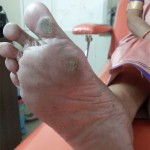
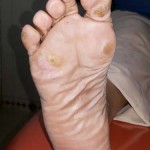
Calluses are the thickening of the skin, typically as a result of excess pressure and repeated rubbing, such as from a shoe or sock. The rubbing causes the skin to produce a layer of protective skin (a callus). They tend to form along the ball of the foot, heel or the underside of the big toe. Calluses tend to be more common in women than men because of the poorly fitting footwear that puts pressure on certain areas of foot. Calluses vary in size, and can become painful.
Diabetic patients are more prone to develop callosities and also other medical conditions. Deep ulcers or wound can develop if the callus is left untreated.
Symptoms
The main symptom of a callus is the hardening and thickening of the surface, commonly found on the pressure areas on the foot.
Prevention
The best way to prevent the formation of calluses is to wear proper fitting footwear, particularly avoiding high heeled shoes. Regularly moisturising the foot in order to soften calluses. Use of customised orthotics can be useful to relieve pressure areas.
Possible Treatment
Non-surgical removal of callosities, proper fitting footwear and custom made orthotics.
Corns
Condition and Causes
A “corn” is a small circular thickened lesion in the skin of the foot. It usually forms due to repeated pressure on the skin, such as the rubbing of a shoe. The name “corn” comes from its resemblance to a kernel of corn. A corn is different from a callus in that it has a central core of hard material.
People with foot deformities, such as hammertoes, often suffer from corns because the tops of the bent toes rub against the tops of shoes.
Symptoms
Corns usually result in pain, swelling, or redness and are subject to irritation. Commonly found on top or between toes as well as on the plantar aspect of the foot. Corns are usually very painful.
Prevention
Avoiding footwear that is either too tight or loose and wearing shoes with deeper toe boxes will aid in the prevention of the development of corns.
- Do not use corn caps or pads.
- Avoid home surgeries.
Possible Treatment
There are a number of treatment options from non-surgical debridement to surgical removal of corns. When corns get hard enough to cause pain, you will be recommended the treatment option most appropriate for you. However, if the underlying cause of the corn is not treated or removed, the corn may return. It is important to avoid trying to remove a corn at home or using medicated corn pads, as serious infection may occur.
As a first line of treatment, you may be advised to pare down the corn non-surgically along with appropriate footwear and/or customised orthotics.